

(s) travelled would be equal to the average velocity (half way between the ve- locities at 2 endpoints, where g is the average acceleration due to gravity on earth, for which the ac- cepted value is 9.81m/s. Furthermore, for an object undergoing a constant acceleration, the distance Solving for the change in position ( or distance, s, travelled) from eq. 2) change in time (t-to) change in time (t- to) Where to is the time that the clock started (usually assumed to be 0 seconds). 1) a = change in velocity = (v - vo) (eq. These are given by: y = change in position = (x-xo) (eq. From these measurements, the program records the velocities and the corresponding times An object's motion at any point in time, t, can be described by its position, x, (with respect to a reference starting point, xo) its velocity, v, and its acceler- ation, a. This timing continued until all eight bars passed through the Photo- gate. As the Picket Fence passed through the Photo- gate, the LabPro interface measured the time from the leading edge of one bar blocking the beam until the leading edge of the next bar blocked the beam. A piece of clear plastic with evenly spaced black bars on it, called a Picket Fence was dropped. It can detect whenever this beam is blocked. The Photogate has a beam of infrared light that travels from one side to the other. In this experiment, a very precise timer was connected to the Lab Quest and a Photogate. Physics students measure the acceleration due to gravity using a wide variety of timing methods. This acceleration is usually represented with the symbol, g.
ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY LAB FREE
As a result, an object in free fall accelerates downward at a constant rate. When the object in free fall is near the surface of the earth, the gravitational force on it is nearly con- stant.
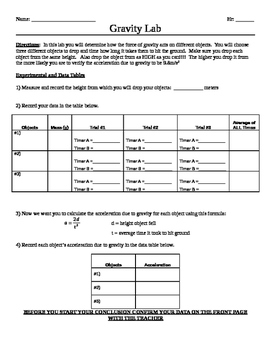
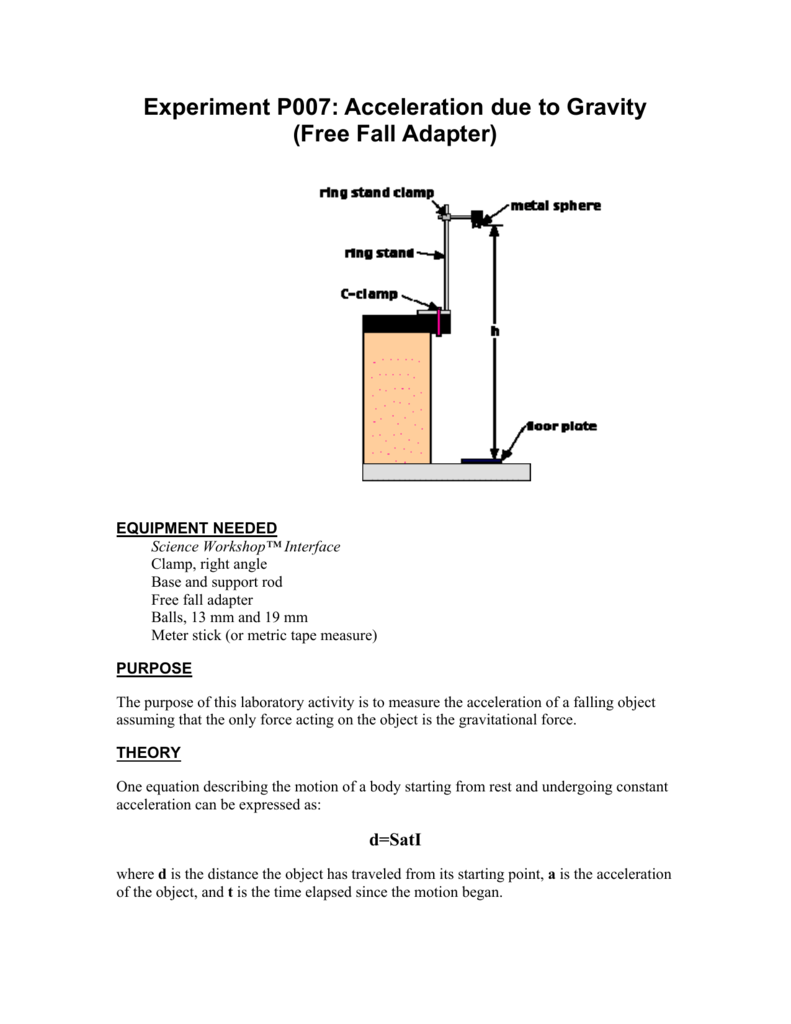
No other forces can be acting in particular, air resistance must be either absent or so small as to be ignored. Introduction Figure 1 Theory: We say an object is in free fall when the only force acting on it is the earth's gravitational force. LAB 3 ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY Picket tence Aim: Measure the acceleration of a freely falling body (g) using a Picket Fence and a Photogate.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
